Domain aliases are domains that you own, but which do not contain any content. Instead, they point to the contents of another domain or subdomain on your account.
Ordering an alias domain
Alias domains can be ordered via My Zone. Under the Webhosting menu choose Webserver and then click on Order alias.
The domain owner will be verified while adding an alias, this eliminates the possibility of maliciously redirecting someone else’s domain.
Viewing existing aliases
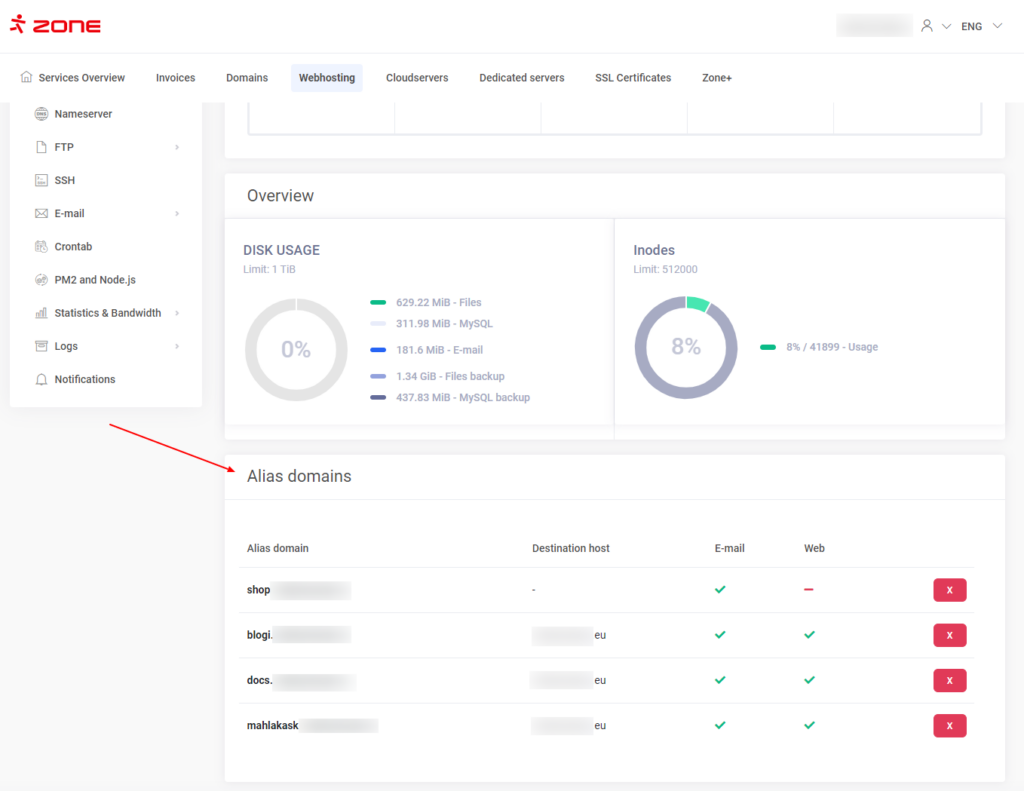
You can view active aliases via Webhosting and then the Server dashboard. Active aliases are shown under Alias domains.
You can see the name of the alias domain aswell as the destination host. Should you wish to delete the alias, simply click on the red X button.
Main domain
The main domain is a virtual server that is hosted by a paid service package. Added alias domains are free of charge. There is no limit on the number of added aliases.
Technical
Technically, the Alias is added as a directive to the ServerAlias of the Apache web server. When the client makes a request for an alias domain, the same domain will remain visible in the address bar of the browser and no automatic redirection will be performed on the server side. However, if the redirection to the main domain does occur, it will be done by the application (e.g. WordPress) itself.
SSL certificate
If a Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate is in use on the main domain, all alias domains are automatically added to the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) list (this only happens if the alias is actually pointed to the server and the server can prove the right to use the alias domain name).
If an alias domain exists, all email addresses are automatically directed to the main domain. For example, if there is an address info@maindomain.eu, emails sent to info@aliasdomain.eu will reach both mailboxes.
You are allowed to send emails from @aliasdomain.eu address via webmail and smtp
Displaying different content on alias domains
By default, alias domains always display the contents of the main domain. If you want to display different content on, there are two options:
a) Adding an alias to a subdomain
This is technically the easiest way. For example, you have a subdomain alias.maindomain.eu, you can add the alias to that subdomain and it will display the contents of the subdomain (e.g. WordPress). Emails are redirected to the mailboxes of the main domain.
b) Direct .htaccess queries to various scripts.
This option requires technical skills. Examples of .htaccess rewrite rules.
Redirection
Should you wish to redirect all adomains to the main domain, you should make an .htaccess file with commands to redirect the connection request to the main domain (if the request is not for the main domain).
Example:
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^maindomain.eu$ [NC]
RewriteRule .* https://maindomain.eu%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]